The losses of power distribution networks are a high percentage of the total losses of the electrical network. According to this issue, investing in reducing energy losses can free up production capacity. This means that by making appropriate and engineered investments, instead of building expensive power plants, the losses of the electrical network can be reduced.
For this purpose, while reviewing the required basic information, the computational basis of the proposed plans and their classification model should be described and then the operational method should be presented to identify the projects that are in the form of early efficiency loss reduction plans. Then, the size of the proposed projects and the required initial investment cost are determined, and at the end, the amount and value of energy losses reduced, the period of return on investment of the proposed projects and their impact on the
reduction of energy losses of the entire evaluated area are presented
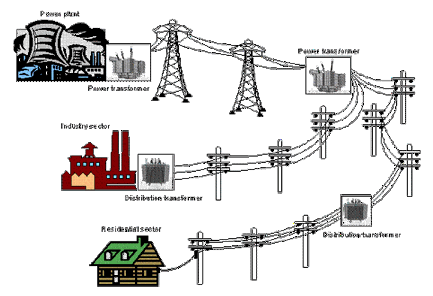
Losses in distribution networks
- Network technical losses
- Non-technical network losses
One of the important aspects of designing distribution networks is the optimal design of the network in order to reduce losses. Several factors such as the lack of proportional load distribution between different feeders of a post in the electrical energy distribution network, the high ratio of resistance to inductive reactance of the lines and the large number of circuits and transformers compared to the
The main reasons for losses and their increase in power distribution networks
:The most important reasons for the occurrence and increase of losses in electricity distribution networks are
* The asymmetry of the load of the phases in the weak pressure network (in some cases, operators connect branches to one phase, which causes high current to pass through one phase and low current to other phases.)
* Load imbalance of low pressure and medium pressure feeders-
* Low power factor (the lower the power factor, the higher the reactive power passing through the conductors, and with the increase of the reactive power passing through the conductors, the current passing through the conductors and as a result the losses in the network will increase.)
* Improper use of the capacity of transformers and high capacity substation design in order to predict the increase in load in the future (transformer losses include pregnancy losses and no-load losses. Among the network equipment, the most losses are related to transformers, and these losses depend on the technical specifications and point The work of the transformer will be different.)
* Lack of attention to the correction, improvement and development of the network
* High capacity of capacitors
* Low network voltage (voltage drop increases losses because losses depend on the passing current and the passing current depends on the voltage and the passing power. For example, if the voltage decreases by 10%, the losses increase by 23%.)
* Not having a long-term comprehensive plan
* The use of low wire sections in low pressure networks (ohmic losses) (the average reduction in losses due to the change in cross section from 25 to 35 or 50 and from 35 to 50 is about 2 to 3%. Also, if the neutral wire with If the cross section equal to the phase wire is used, the losses for ground resistance will be reduced by 20%.)
* Lack of long-term investment in the production, transmission and distribution sectors
* Not having a regular schedule of timely service of lines, transformers and other equipment
* Unauthorized branches
* Current leakage (includes leakage through insulators and tree branches.)
* Deterioration of the equipment of lines and substations (due to the proximity of the network and electrical equipment with corrosive factors as well as the passage of current, the network will be worn out and thus the amount of losses in the equipment will increase)
Common loss reduction methods
. Balancing the load of weak pressure network phases-
. Balancing the length of weak pressure feeders by moving the open points-
. Reorganization of the weak pressure network and construction of new lines in line with it-
.Correcting the power factor by installing a fixed capacitor in the low pressure network and the medium pressure network in a fixed or. .controlled manner
. Modifying the cross section of low voltage network conductors-
. Moving air transformers and transferring them to the center of gravity of the load if possible-
. Modification of the subscriber service cable-
. Replacing or repairing loose and inappropriate connections (hot spots)-
. Construction of a new 20 kV air or ground substation and rearrangement of the low voltage network according to it-
. The use of low-capacity and low-loss transformers to partially eliminate the weak pressure network-
. Rearranging the medium pressure network in order to equalize the length or load of the medium pressure feeders-
.Construction of a new medium pressure feeder to reduce the feeding radius of the existing network and balance the existing load-
transmission network, cause an increase in losses in these networks-
.